 |
QUICK SEARCH
MO PROJECTS:
Africa
Asia/Pacific
Mesoamerica
North America
South America
General Taxonomy
Photo Essays
Training in Latin
America
MO RESEARCH:
Wm. L. Brown Center
Bryology
GIS
Graduate Studies
Research Experiences
for Undergraduates
Imaging Lab
Library
MBG Press
Publications
Climate Change
Catalog Fossil Plants
MO DATABASES:
W³MOST
Image Index
Rare Books
Angiosperm
Phylogeny
Res Botanica
All Databases
INFORMATION:
What's New?
People at MO
Visitor's Guide
Herbarium
Jobs & Fellowships
Symposium
Research Links
Site Map
Search
Deforestation and plant diversity of |
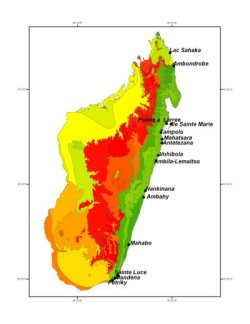 Littoral forest shapefile |
The eastern littoral forest, which biogeographically corresponds to sites near sea level on sand within Madagascar's humid bioclimatic region, is one of the most highly threatened and impacted vegetation types in the country, and is almost surely condemned to extinction unless immediate steps are taken to preserve it.
Change in littoral forest cover from original to current extent was estimated using Geographical Information System (GIS) tools, remote sensing data (both satellite imagery and low elevation digital photography), and environmental data layers. Our results indicate that 10.3% of the original littoral forest remains in the form of small forest parcels, and that only 1.5% of these remaining fragments are included within the existing protected areas network. (Consiglio, T. et al, (2006) Conservation Biology 20: 1799-1803).
Additionally, ca. 13% of Madagascar's total native flora has been recorded from what was originally less than 1% of its total land surface, and that over 25% of the ca. 1,574 plant species known from littoral forests are endemic.
However, in 2003 at the World Parks Congress in Durban, South Africa, Madagascar's President Marc
Ravalomanana charged his government and its NGO partners with formulating recommendations for the
addition of 4.5 million hectares to the protected areas network. The first set of areas proposed
by a governmentally appointed advisory group for this initiative in early 2005 includes 15 parcels of
littoral forest totaling 19,880 ha, which represents 41.5% of remaining littoral forest.
![]()
 Aerial Image Metadata |
© 1995-2025 Missouri Botanical Garden, All Rights Reserved
4344 Shaw Blvd.
St. Louis, MO 63110
(314) 577-5100
Technical Support
